The security of Windows Servers is crucial in today’s interconnected world. With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, the risk of a server being hacked is a constant concern for IT administrators. Early detection of a security breach can mitigate damage and prevent data loss. This article provides a detailed guide on how to detect if your Windows Server has been hacked, including signs to watch for, tools to use, and steps to take to ensure your server’s security.
Understanding the Importance of Server Security
Windows Servers are often the target of cyberattacks because they store critical data and support essential business functions. A successful breach can lead to data theft, financial loss, and operational disruption. Hackers use various methods to infiltrate servers, including exploiting vulnerabilities, phishing attacks, and brute-force attacks. Recognizing the signs of a hack early on is essential for minimizing damage and restoring security.

Common Indicators of a Hacked Windows Server
Unusual Network Activity
One of the first signs of a compromised server is abnormal network traffic. An unexpected spike in outgoing or incoming traffic can indicate that your server is being used for malicious activities, such as a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack or data exfiltration.
Unauthorized Logins and User Accounts
Regularly check your server’s login records for unusual patterns, such as logins at odd hours or from unfamiliar IP addresses. Additionally, new user accounts that you did not create can be a red flag.
System Performance Issues
A hacked server often experiences performance degradation. If your server becomes unusually slow, crashes frequently, or exhibits erratic behavior, it could be due to malicious processes consuming system resources.
Changes in Configuration and Files
Unexplained changes in system settings, configuration files, or application behaviors can signal a security breach. Look for modified or newly created files and directories that you did not authorize.
Security Tool Alerts
Keep an eye on alerts from your security tools, such as antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems (IDS). These tools can provide early warnings of potential threats.
The steps on how to troubleshoot if the Windows server has been hacked.
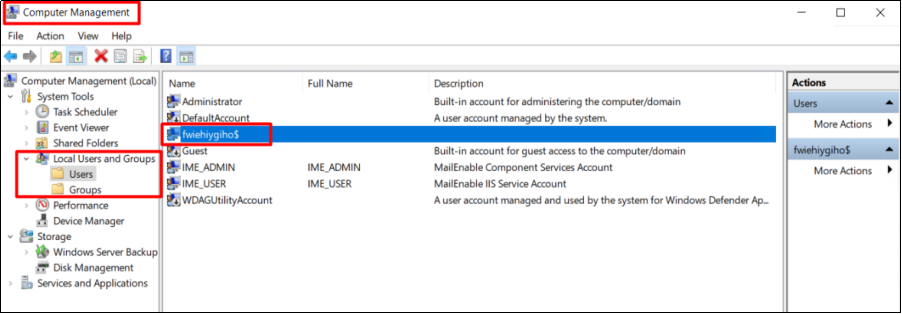
1. Check for hidden users or abnormal users
Open Computer Management -> Local Users and Groups. Check the name of the user/user group. If the name contains a special symbol, such as $ or gibberish, it indicates that the user/user group is hidden and vulnerable to hacking.
If there are abnormal users or groups, please delete them.
2. Check abnormal processes
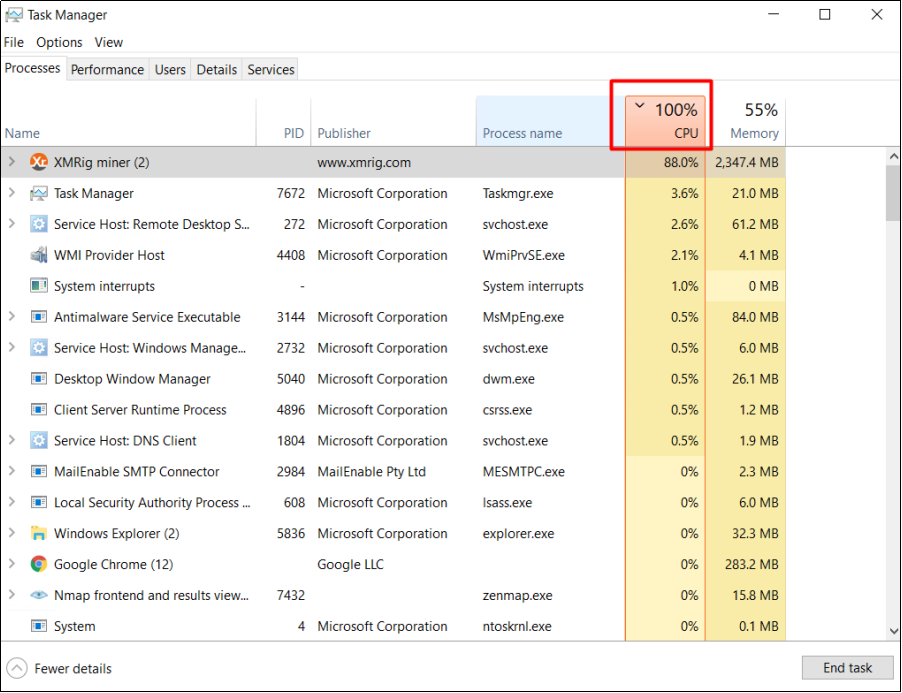
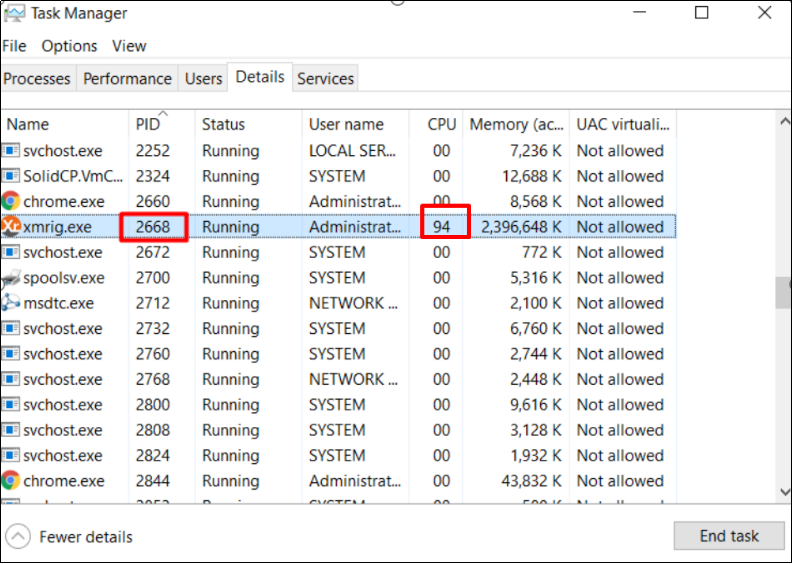
Check processes with high CPU and memory usage
Abnormal processes may cause high CPU or memory usage. The Xmrig.exe process, as the screenshot shows, might be uploaded by a hacker.
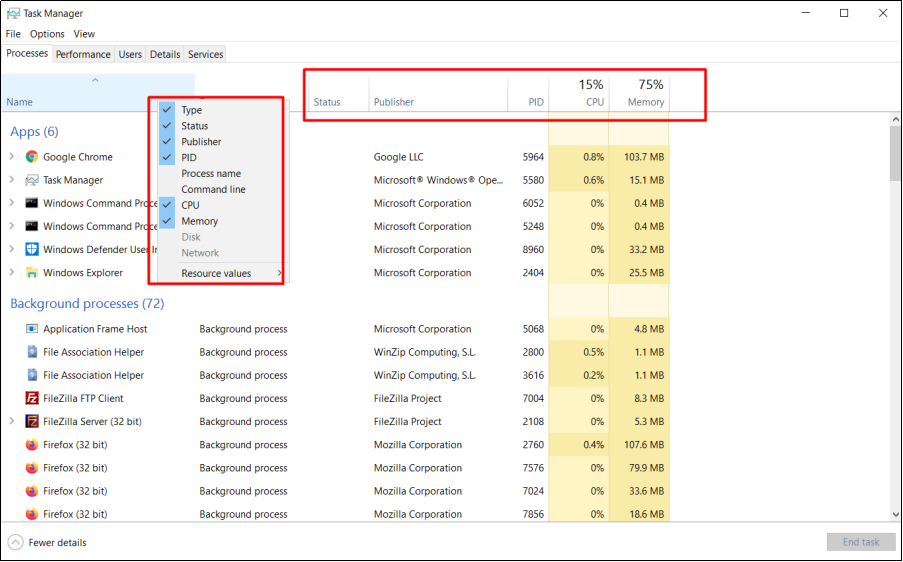
Check processes with suspicious publishers
Right-click on the top menu to find out the name of the application publisher as highlighted below. Notice any suspicious processes and carry out further investigations. The following shows how to enable the menu of Type, Status, Publisher, PID, and so on.
Check processes with abnormal connections
Open the command prompt on your PC and type “netstat -ano” to check all connections. If there are many connections from the same PID, please enter command tasklist |findstr “pid” to check the related services that use the PID.
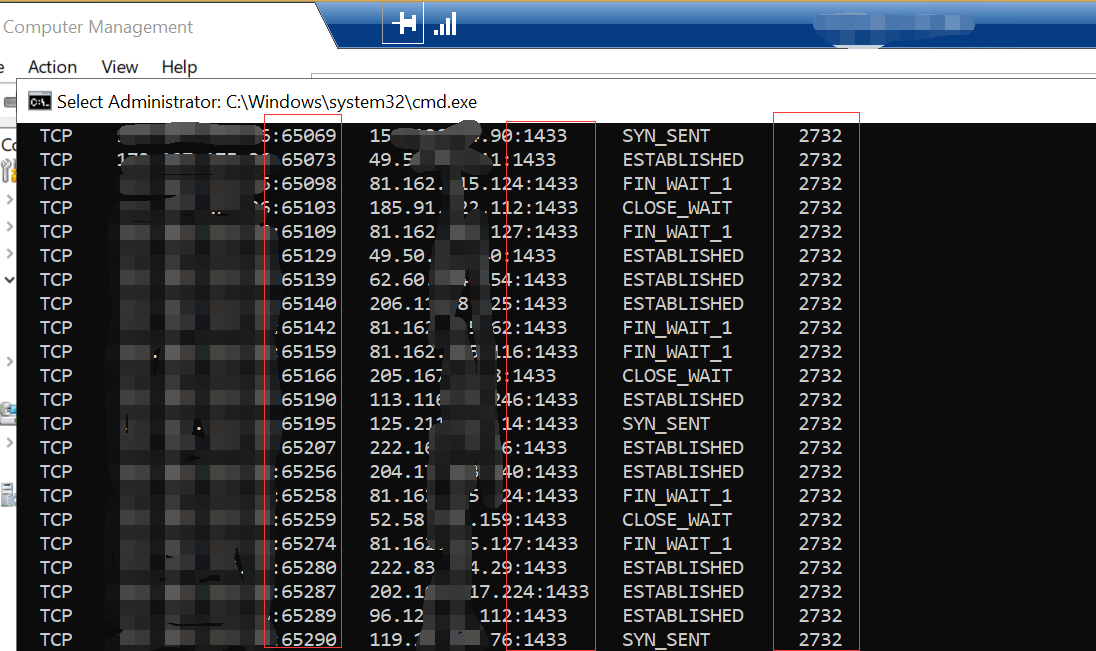
End abnormal processes
If you identify a malicious process, right-click on the process name and click “End Process Tree”. Choose “Open file location” to delete the abnormal files. This disconnects your server from the suspicious connections and all its dependencies. The following shows how to end a process.
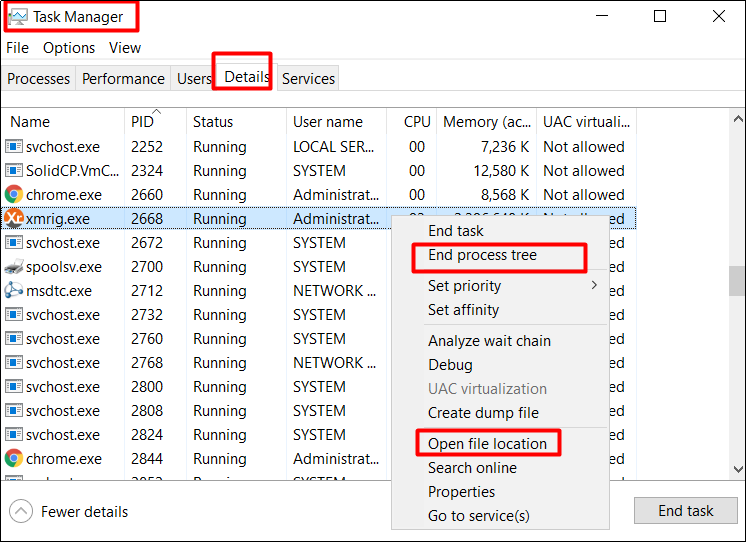
3. Check Windows system directories
Check the system directories in Windows such as “C:Windows” and “C:WindowsSystem32”. If there are abnormal scripts or executable files in your server as the screenshot shows, your server probably has been hacked.
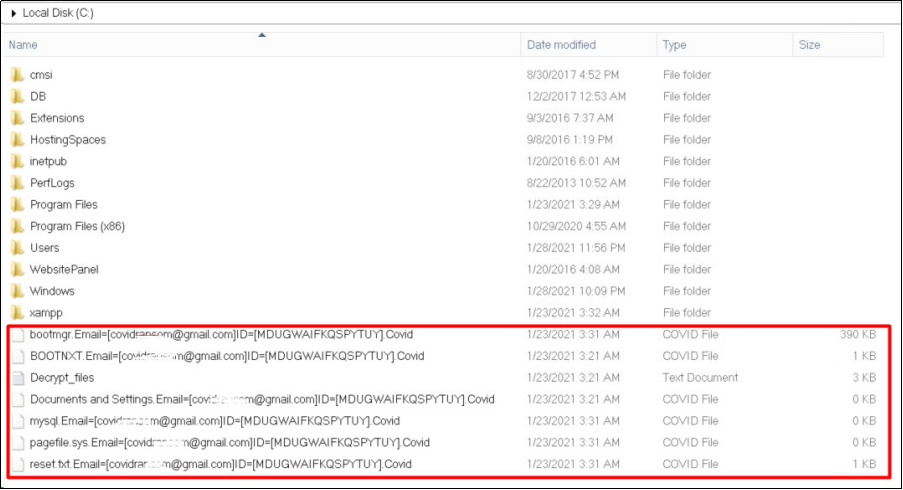
4. Check firewall rules
Check whether there are garbled firewall rules or strange ports opened. If there are abnormal firewall rules, please delete them. An example of abnormal firewall rules is shown below.
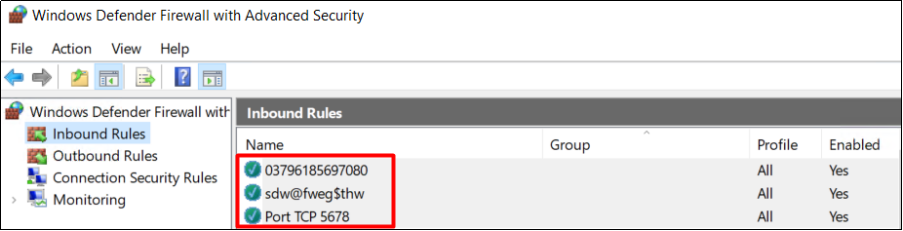
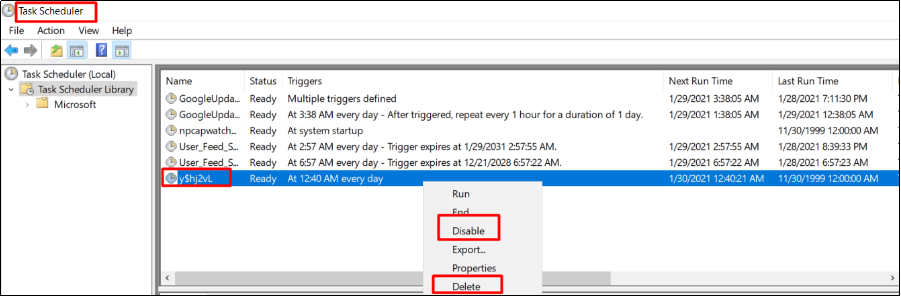
5. Check tasks in Task Scheduler
Go to the start menu, enter “task scheduler” and open it. Check if there are abnormal tasks listed in the library. If there are abnormal tasks, please disable and delete them. The following shows how to disable and delete a task.
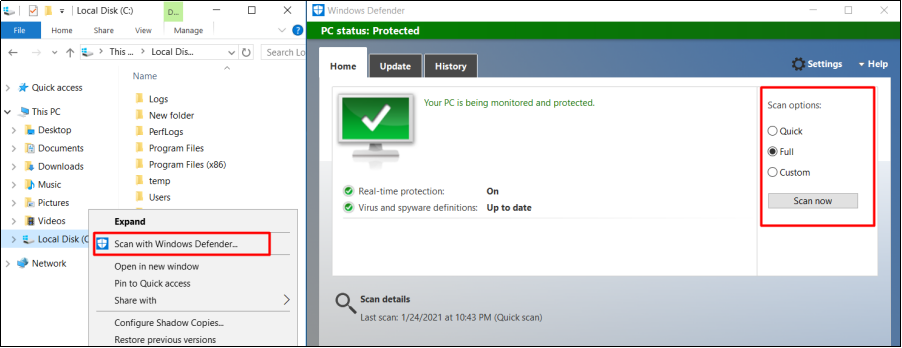
6. Scan all drives through Windows Defender
If the server is based on Windows Server 2016/2019, clients can use Windows Defender to scan the server. Click Clean up if any suspicious files are found after scanning.
Detecting a hack on your Windows Server requires vigilance and the use of various tools and methods. By understanding the common signs of a breach, employing effective detection tools, and taking swift action when a hack is detected, you can protect your server and minimize potential damage. Moreover, implementing proactive security measures can help prevent future attacks, ensuring the safety and integrity of your critical systems and data.
Conclusion
In the above article, we’ve covered how to detect if your Windows Server has been hacked by identifying key indicators and the steps on how to troubleshoot if the windows server has been hacked. We hope these insights help you effectively secure your server and prevent potential breaches.
For more in-depth tips and tutorials on Windows Server security and administration, stay connected with our blog. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please contact WindowsVPSCheap Customer Support.
CATEGORY:Knowledge

